PuTTY: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
DRSDavidSoft (talk | contribs) (Added initial page) |
DRSDavidSoft (talk | contribs) m (Updated formatting) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
# '''Identify the Serial Port''': | # '''Identify the Serial Port''': | ||
#*'''On Windows''': Check the assigned COM port via Device Manager under "Ports (COM & LPT)". | |||
#*'''On Linux/macOS:''' Use <code>ls /dev/tty*</code> to identify the appropriate device (e.g., <code>/dev/ttyUSB0</code>). | |||
#'''Launch PuTTY:''' | |||
#*Open the PuTTY application. | |||
#'''Configure Connection Settings''': | |||
#*Under the "Session" category: | |||
#**'''Connection type''': Select '''Serial'''. | |||
#**'''Serial line''': Enter the appropriate port (e.g., <code>COM3</code> or <code>/dev/ttyUSB0</code>). | |||
#**'''Speed''': Set the baud rate (e.g., <code>115200</code>). | |||
#'''Set Serial Parameters''': | |||
#*Navigate to "Connection" → "Serial": | |||
#**'''Data bits''': Typically <code>8</code>. | |||
#**'''Stop bits''': Typically <code>1</code>. | |||
#**'''Parity''': Usually <code>None</code>. | |||
#**'''Flow control''': Often set to <code>None</code>. | |||
#'''Initiate Connection''': | |||
#*Click '''Open''' to start the session. | |||
===Session Logging=== | |||
To record session output: | |||
# ''' | #During an active session, right-click on the PuTTY window title bar and select '''Change Settings'''. | ||
#Navigate to "Session" → "Logging". | |||
#Choose '''All session output'''. | |||
#Specify a log file location and name. | |||
#Click '''Apply''' to start logging. | |||
===Best Practices=== | |||
*'''Connect Ground First''': Always establish a common ground between devices before connecting TX/RX lines. | |||
*'''Cross TX/RX Lines''': Connect the adapter's TX to the device's RX, and vice versa. | |||
*'''Verify Voltage Levels''': Ensure compatibility between the adapter's logic level and the target device to prevent damage. | |||
*'''Avoid Backfeeding Power''': If the target device is self-powered, do not connect the adapter's VCC line. | |||
===Features=== | |||
*🖥️ '''Cross-platform''': Available mainly for Windows, can also be used under Linux, and macOS. | |||
*🔌 '''Serial Communication''': Supports direct connections to serial ports. | |||
*🛠️ '''Customizable Settings''': Configurable baud rate, data bits, parity, stop bits, and flow control. | |||
*📄 '''Session Logging''': Ability to log session output for debugging purposes. | |||
*💾 '''Session Management''': Save and load session profiles for repeated use. | |||
===External Resources=== | |||
*[https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/ Official PuTTY Website] | |||
*[https://documentation.help/PuTTY/ PuTTY User Manual] | |||
*[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=29MZCza_dOs Video Tutorial: Using PuTTY for Serial Communication] | |||
=== External Resources === | |||
* [https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/ Official PuTTY Website] | |||
* [https://documentation.help/PuTTY/ PuTTY User Manual] | |||
* [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=29MZCza_dOs Video Tutorial: Using PuTTY for Serial Communication] | |||
[[Category:Serial Communications]] | [[Category:Serial Communications]] | ||
[[Category:Terminal Emulators]] | [[Category:Terminal Emulators]] | ||
[[Category:Hardware Debugging Tools]] | [[Category:Hardware Debugging Tools]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:38, 15 May 2025
PuTTY as a Serial Terminal
PuTTY is a free and open-source terminal emulator developed by Simon Tatham. While widely known for SSH and Telnet capabilities, it also functions effectively as a serial console, making it invaluable for interfacing with embedded systems, routers, and microcontrollers via UART.
Establishing a Serial Connection
To connect to a device via serial using PuTTY:
- Identify the Serial Port:
- On Windows: Check the assigned COM port via Device Manager under "Ports (COM & LPT)".
- On Linux/macOS: Use
ls /dev/tty*to identify the appropriate device (e.g.,/dev/ttyUSB0).
- Launch PuTTY:
- Open the PuTTY application.
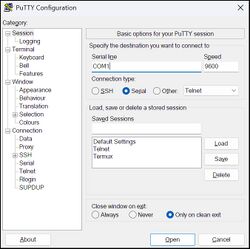
- Configure Connection Settings:
- Under the "Session" category:
- Connection type: Select Serial.
- Serial line: Enter the appropriate port (e.g.,
COM3or/dev/ttyUSB0). - Speed: Set the baud rate (e.g.,
115200).
- Under the "Session" category:
- Set Serial Parameters:
- Navigate to "Connection" → "Serial":
- Data bits: Typically
8. - Stop bits: Typically
1. - Parity: Usually
None. - Flow control: Often set to
None.
- Data bits: Typically
- Navigate to "Connection" → "Serial":
- Initiate Connection:
- Click Open to start the session.
Session Logging
To record session output:
- During an active session, right-click on the PuTTY window title bar and select Change Settings.
- Navigate to "Session" → "Logging".
- Choose All session output.
- Specify a log file location and name.
- Click Apply to start logging.
Best Practices
- Connect Ground First: Always establish a common ground between devices before connecting TX/RX lines.
- Cross TX/RX Lines: Connect the adapter's TX to the device's RX, and vice versa.
- Verify Voltage Levels: Ensure compatibility between the adapter's logic level and the target device to prevent damage.
- Avoid Backfeeding Power: If the target device is self-powered, do not connect the adapter's VCC line.
Features
- 🖥️ Cross-platform: Available mainly for Windows, can also be used under Linux, and macOS.
- 🔌 Serial Communication: Supports direct connections to serial ports.
- 🛠️ Customizable Settings: Configurable baud rate, data bits, parity, stop bits, and flow control.
- 📄 Session Logging: Ability to log session output for debugging purposes.
- 💾 Session Management: Save and load session profiles for repeated use.